Distributed system architectural styles (Messaging)
Jan 2013
The intention of this post is to discuss the following styles founded on messaging:
- Service Broker
- Service Bus
SOA can be built on top of any of these styles (but not limited, i.e. non message based infrastructure).
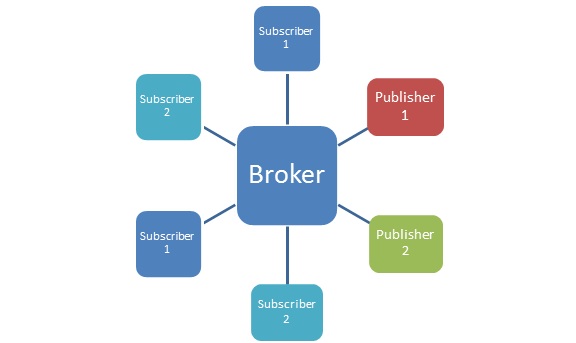
Service Broker
Characteristics:
- Broker is physically separate.
- All communication goes through the broker.
- Broker handles failover, routing, data transformation.
Advantages:
- Attempt to handle spatial coupling (not as well as bus), however problem introduced - centralised routing.
- Concentrating all communications to a single logical entity, enables central management.
- Enables “intelligent” routing, data transformation, orchestration.
- Doesn’t require changes to surrounding apps.
Disadvantages:
- The broker is a single point of failure, must be robust and performant. But can be overcome using redundancy – which in turn introduces complexity.
- Business logic is centralised.
- Procedural programming at a large scale, without good unit testing or source control.
- Lack of accountability, which is the single source of truth?
- Cannot differentiate between logical and physical endpoint.
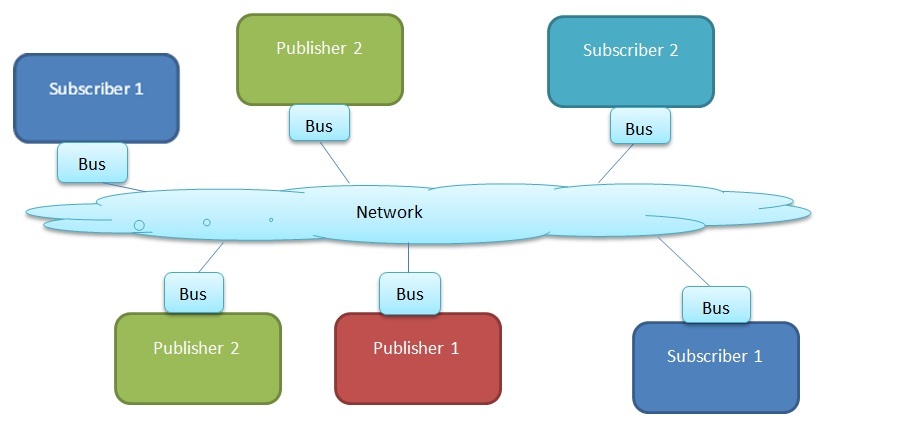
Service Bus
Characteristics:
- Bus is not necessarily physically separate (Think of it like a wireless card on the network).
- Communication is distributed (No single point of failure).
Advantages:
- No single point of failure.
- Bus is simpler – no routing or service fail over.
- Doesn’t break service autonomy.
-
Reduces spatial coupling: »“when one service is moved from one server to another this will not stop communications to that service” - Udi Dahan
- Allows one logical endpoint to scale out to multiple physical endpoints.
Disadvantage:
- More difficult to design distributed solutions than centralised ones.